


Australian Biological Resources Study
| Checklist of the Lichens of Australia and its Island Territories | ||
| Introduction | A–D | E–O | P–R | S–Z | Oceanic Islands | References | ||
| Pseudocyphellaria glaucescens (Kremp.) Imshaug | ||
| Adapt. Antarctic Ecosys. 964 (1977); Sticta glaucescens Kremp., Verh. K.K. Zool.-Bot. Ges. Wien 30: 335 (1880). T: Australia, s. loc., coll. unknown; holo: M; iso: MEL. | ||
| Thallus irregularly spreading, loosely attached centrally, 5–8 (–12) cm wide; margins free. Lobes linear-laciniate, very variable, 1–5 (–8) cm long, 2–8 (–12) mm wide, ±dichotomously to irregularly branched, discrete or contiguous at margins, imbricate centrally, tough, rigid when dry, pliable when wet, rather thin, not coriaceous; apices divergent; lobe margins entire, noticeably thickened, ridged below, without projecting pseudocyphellae. Upper surface glaucous olive to greyish glaucous when dry, olive-green suffused yellowish when wet, faveolate with rounded interconnecting ridges, ±canaliculate towards apices; without isidia, maculae, phyllidia, pseudocyphellae or soredia. Medulla mainly yellow to partly yellow-white. Photobiont green. Lower surface pale yellowish or yellow-white at margins, darkening to mustard-yellow, buff-brown to red-brown centrally, mainly glabrous or with scattered thin white silky tomentum centrally, strongly wrinkled, bullate or puckered. Pseudocyphellae scattered, to 0.2 mm diam.; margins swollen; pore minute; decorticate area yellow. Apothecia marginal, sessile to subpedicellate, 0.5–2 (–2.5) mm diam., deeply cupuliform to ±plane; disc dark red-brown to black, matt, occasionally finely white-pruinose; exciple pale buff or pinkish, corrugate-scabrid, persisting as a coarsely irregularly crenate-stellate structure; epithecium red-brown, K–; hymenium pale straw-yellow or colourless; amphithecium bright yellow; hypothecium opaque, yellow-brown, K–. Ascospores fusiform-ellipsoidal, polarilocular, 22–28 × 8.5–11 µm, brown or olive; septum 2.5–3 µm thick. CHEMISTRY: Pulvinic acid, pulvinic dilactone, calycin, pulvinamide, methyl evernate, tenuiorin, methyl lecanorate, methyl gyrophorate (major), methyl oviate, 2'-O-methyltenuiorin, 2"-O-methyltenuiorin, 2',2"-di-O-methyltenuiorin, evernic acid, gyrophoric acid, stictic acid (major), constictic acid, 9α-acetoxyconstictic acid, norstictic acid, hopane-6α,7β,22-triol (major), 6α-acetoxyhopane-7β,22-diol (minor) and 7β-acetoxyhopane-6α,22-diol (minor). | 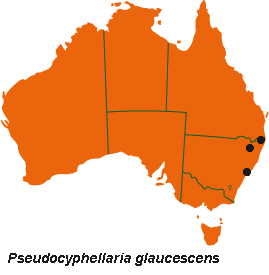 |
|
| A rare Australian endemic growing on twigs and branches of forest trees in eastern New South Wales; also in Lord Howe Is. | ||
| Galloway et al. (2001) | ||
| Checklist Index |
| Introduction | A–D | E–O | P–R | S–Z | Oceanic Islands | References |
This work is copyright. Apart from any use as permitted under the Copyright Act 1968, no part may be reproduced by any process without prior written permission from Australian Biological Resources Study. Requests and inquiries concerning reproduction and rights should be addressed in the first instance to Dr P. McCarthy. These pages may not be displayed on, or downloaded to, any other server without the express permission of ABRS.