


Australian Biological Resources Study
| Checklist of the Lichens of Australia and its Island Territories | ||
| Introduction | A–D | E–O | P–R | S–Z | Oceanic Islands | References | ||
| Xanthoparmelia hypoleiella Elix | ||
| Mycotaxon 65: 488 (1997). T. Western Australia. Coolgardie, 30°57'S, 121°09'E, 350 m, on rock, H. A. Morrison; holo: MEL 1026882. ****Xanthoparmelia hypoleia (Nyl.) Hale, Phytologia 28: 487 (1974) [Australian records]; Parmelia hypoleia Nyl., Syn. Meth. Lich. 1: 393 (1860) [Australian records]. | ||
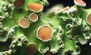
| Thallus foliose, adnate, to 5–8 cm wide. Lobes imbricate or not, flat, sublinear-elongate, subdichotomously to irregularly branched, 0.5–1.5 (–3) mm wide. Upper surface yellow-green, blackening with age, shiny, with distinct or effigurate maculae, lacking isidia and soredia; older lobes becoming rugulose and developing transverse cracks; lobes often black-margined, particularly towards apices. Medulla white. Lower surface black; rhizines moderately dense, simple, tufted or not, robust, 0.5–1.5 mm long, black. Apothecia shortly pedicellate, 3–6 mm wide; disc concave, dark brown; thalline exciple maculate, thick, entire and involute, becoming dentate and cracked. Ascospores 6–8 × 4–5 µm. Pycnidia common. Conidia bifusiform, 6–7 × 0.5 µm. CHEMISTRY: cortex K-, UV-; medulla K+ pale yellow then brown, C-, P+ orange-red; containing usnic acid, protocetraric acid and ±virensic acid (trace). | ||
| Rare in coastal and temperate hinterland zones of south-western W.A. Grows on rock. | ||
| Elix (1994z, 1997b) | ||
| Checklist Index |
| Introduction | A–D | E–O | P–R | S–Z | Oceanic Islands | References |
This work is copyright. Apart from any use as permitted under the Copyright Act 1968, no part may be reproduced by any process without prior written permission from Australian Biological Resources Study. Requests and inquiries concerning reproduction and rights should be addressed in the first instance to Dr P. McCarthy. These pages may not be displayed on, or downloaded to, any other server without the express permission of ABRS.